A Ph.D Biotechnology is a research-oriented doctoral program designed for students who want to build a strong career in scientific research, academics, pharmaceuticals, healthcare, agriculture, and industrial biotechnology. This course focuses on advanced biological sciences combined with modern technologies to develop innovative solutions in medicine, environment, and industry.
Choosing the Right Program and Research Area
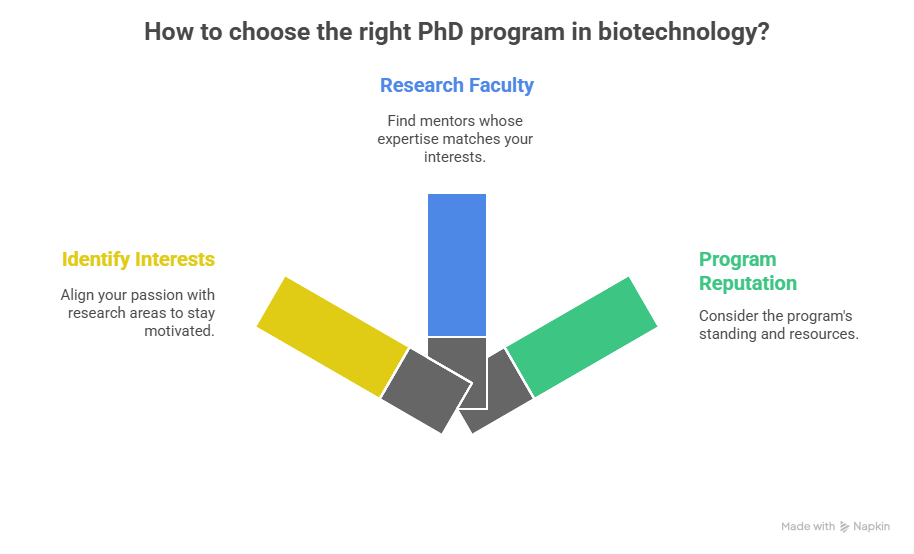
The first and arguably most crucial step is selecting the right Ph.D Biotechnology program and research area. Biotechnology is a broad field, encompassing diverse specializations like genetic engineering, bioprocessing, bioinformatics, and drug discovery.
- Identify Your Interests: What aspects of biotechnology genuinely excite you? Are you passionate about developing new therapies, improving agricultural practices, or understanding the fundamental mechanisms of life? Your passion will fuel your motivation throughout the demanding PhD journey.
- Research Faculty Expertise: Explore the research interests of faculty members in different programs. Look for professors whose work aligns with your interests and whose mentorship style resonates with you.
- Program Reputation and Resources: Consider the program’s reputation, Ph.D Biotechnology funding opportunities, and available resources, such as state-of-the-art equipment and core facilities.
- Location and Environment: Think about the location of the university and the overall environment. A supportive and collaborative environment can significantly impact your well-being and research productivity.
- Talk to Current Students: Reach out to current Ph.D Biotechnology students in programs you’re interested in. They can provide valuable insights into the program’s strengths, weaknesses, and overall culture.
Coursework and Qualifying Exams
The initial years of a PhD program typically involve rigorous coursework designed to provide a strong foundation in core biotechnology principles and specialized areas.
- Core Courses: Expect to take courses in molecular biology, biochemistry, genetics, cell biology, and biostatistics.
- Specialized Courses: Depending on your research area, you may take courses in areas like immunology, virology, metabolic engineering, or computational biology.
- Qualifying Exams: Most programs require students to pass qualifying exams (also known as candidacy exams) to demonstrate their mastery of the subject matter and their ability to conduct independent research. These exams can be written, oral, or a combination of both.
- Strategies for Success: Attend lectures regularly, actively participate in discussions, form study groups, and seek help from professors and teaching assistants when needed.
Research: The Heart of the PhD
Research is the cornerstone of a PhD program. It’s where you apply your knowledge, develop your skills, and make original contributions to the field.
- Choosing a Research Project: Work closely with your advisor to define a research project that is both intellectually stimulating and feasible within the timeframe of your Ph.D Biotechnology.
- Developing Research Skills: Learn essential research techniques, such as experimental design, data analysis, and scientific writing.
- Time Management and Organization: Develop effective time management and organizational skills to manage your research activities, experiments, and data.
- Troubleshooting and Problem-Solving: Research is inherently challenging. Learn to troubleshoot experiments, analyze unexpected results, and develop creative solutions to overcome obstacles.
- Collaboration and Communication: Collaborate with other Ph.D Biotechnology researchers, attend conferences, and present your work to the scientific community. Effective communication is crucial for disseminating your findings and building your professional network.
Navigating the PhD Journey: Challenges and Strategies
The PhD journey is not without its challenges. It requires resilience, perseverance, and a proactive approach to problem-solving.
- Dealing with Stress and Burnout: PhD students often face high levels of stress and burnout. Prioritize self-care, maintain a healthy work-life balance, and seek support from mentors, counselors, or support groups.
- Managing Advisor Relationships: Building a strong and productive relationship Ph.D Biotechnology with your advisor is essential. Communicate openly, seek feedback regularly, and address any conflicts constructively.
- Overcoming Imposter Syndrome: Many PhD students experience imposter syndrome, the feeling that they are not good enough or that they don’t belong. Recognize these feelings, challenge negative thoughts, and focus on your accomplishments.
- Seeking Mentorship: Find mentors who can provide guidance, support, and advice throughout your PhD journey. Mentors can be senior researchers, alumni, or professionals in your field.
- Networking: Attend conferences, workshops, and seminars to network with other researchers and professionals in the biotechnology industry. Networking can open doors to collaborations, internships, and job opportunities.
Career Prospects After a PhD in Biotechnology
A PhD in Biotechnology opens doors to a wide range of career paths in academia, industry, and government.
- Academia: Pursue a career as a professor, researcher, or lecturer at a university or research institution.
- Industry: Work in research and development, product development, regulatory affairs, or business development at biotechnology companies, pharmaceutical companies, or agricultural companies.
- Government: Conduct research, develop policies, or regulate biotechnology products at government agencies like the National Institutes of Health (NIH), the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), or the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA).
- Other Options: Explore careers in science writing, consulting, intellectual property law, or venture capital.
Ph.D Biotechnology Courses – Doctoral research programs in biotechnology and life sciences
Ph.D in Biotechnology Admission – Application process, exams, and interviews
Biotechnology Ph.D Eligibility – Academic requirements for admission
Biotechnology Research Courses – Advanced research-focused biotechnology programs
Career After Ph.D Biotechnology – Job roles and opportunities after doctoral studies
Final Thoughts
A PhD in Biotechnology is a challenging but rewarding journey. By carefully selecting a program and research area, developing strong research skills, and navigating the challenges along the way, you can achieve your academic and career goals and make a significant contribution to the field of biotechnology. Remember to stay curious, persistent, and passionate about your research, and never hesitate to seek help and support when needed. Good luck!